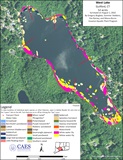
West Lake, Guilford - 2022
West Lake is a 52-acre waterbody located in Guilford, CT. It has a maximum depth of 17 feet with a mucky/organic substrate. The lake is in the Branford River watershed and has an outlet connecting to Clear Lake. It is a private lake with five lake associations and a West Lake Health Committee that works to coordinate lake protection activities. Shoreline development consists of many homes on small lots to the southwest and northeast with larger homes situated further from the lake elsewhere. In these areas most of the shoreline remains forested.
In 2022, West Lake had a diverse aquatic plant community comprised of 20 native species and one invasive (minor naiad). Vegetation occurred to depths of approximately 9 feet (2.5 m) which corresponds to all shoreline areas except for the southeast third of the lake where much of the bottom had plants. Swamp loosestrife occurred along much of the immediate shoreline. As depth increased a progression from water lilies and watershield to submerged plants such as native pondweeds (largeleaf, Robbin’s, small) was common. Minor naiad was not found in 2021 but reappeared in 2022. This was likely a result of its sensitivity to the herbicide applied prior to the 2021 survey. Its locations in 2022 included the northern beach, near transect 1, and on the southeastern shoreline. Because minor naiad is an annual produced from herbicide resistant seeds, this is not unusual. Minor naiad rarely becomes a sufficient nuisance to require management other than manual removal in key areas such as beaches. Phragmites and purple loosestrife are two invasive wetland species we observed in various locations along the shoreline. Because they are not true aquatic plants, they are not included in our aquatic plant analysis.
Native species found in 2022 appeared to be only slightly impacted by past herbicide treatments. Twenty native species were found in 2022 compared to 19 in 2021, 24 in 2010, and 18 in 2005. Plants found in all four CAES IAPP surveys (2005, 2010, 2021 and, 2022) include arrowhead, common bladderwort, large-leaf pondweed, little floating heart, primrose-willow, Robbins’ pondweed, southern naiad, spikerush, spineless hornwort, watershield, white water lily, and yellow water lily. Species not found in 2022 that were found in previous surveys include clasping-leaf pondweed, eelgrass, humped bladderwort, leafy pondweed, lesser bladderwort, low watermilfoil, purple bladderwort, quillwort, and waterwort. Vegetation was roughly as abundant in 2022 as 2021, but less abundant than in 2010 and much less abundant than 2005. The difference in vegetation from 2005 and 2010 from 2022 is mainly due to a large decrease in submersed vegetation such as minor naiad and pondweeds. Suppression of these pondweeds and other species from the past herbicide applications may cease without future management resulting in them becoming a nuisance.
| Species documented in the 2022 survey of West Lake. Scientific Names *Invasive species |
|||
| Grassy arrowhead | Berchtold's pondweed | Cattail | Common bladderwort |
| Globe-fruited false loosestrife | Hidden bladderwort | Large-leaf pondweed | Little floating heart |
| Minor naiad* | Phragmites* | Pickerelweed | Purple loosestrife* |
| Robbins' pondweed | Sedge | Sevenangle pipewort | Small pondweed |
| Snailseed pondweed | Southern naiad | Spikerush | Spineless hornwort |
| Swamp loosestrife | Swamp smartweed | Water smartweed | Watershield |
| White water lily | Yellow water lily | ||